Vaccination and Prevention
Eligibility for HPV Vaccination and Recommended Dosing Schedule
The HPV vaccine represents the most effective strategy to prevent infection with both high-risk and low-risk types of the virus, thereby reducing the incidence of genital warts as well as HPV-associated cancers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that children (both girls and boys) between the ages of 9 and 14 years receive two doses of the vaccine, administered six months apart, ideally prior to the initiation of sexual activity. For women and men aged 15 to 26 years, a three-dose regimen over a six-month period is advised (at months 0, 2, and 6). For individuals aged 27 to 45 years, vaccination may also be considered following consultation with a healthcare professional and assessment of potential benefits.
Optimal Age for HPV Vaccination
Administration of the vaccine is recommended for all children at 11 to 12 years of age.
HPV Vaccination Schedule
According to the recommendations of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the following groups require a three-dose vaccination schedule administered at 0, 1–2, and 6 months:
- Individuals with compromised immune function (such as those with B-lymphocyte antibody deficiency, absence or deficiency of T-lymphocytes, HIV infection, malignant neoplasms, history of transplantation, autoimmune diseases, or those receiving immunosuppressive therapy) who initiate vaccination between the ages of 9 and 26 years.
- Adults who begin HPV vaccination between the ages of 27 and 45 years are also advised to follow the three-dose schedule.
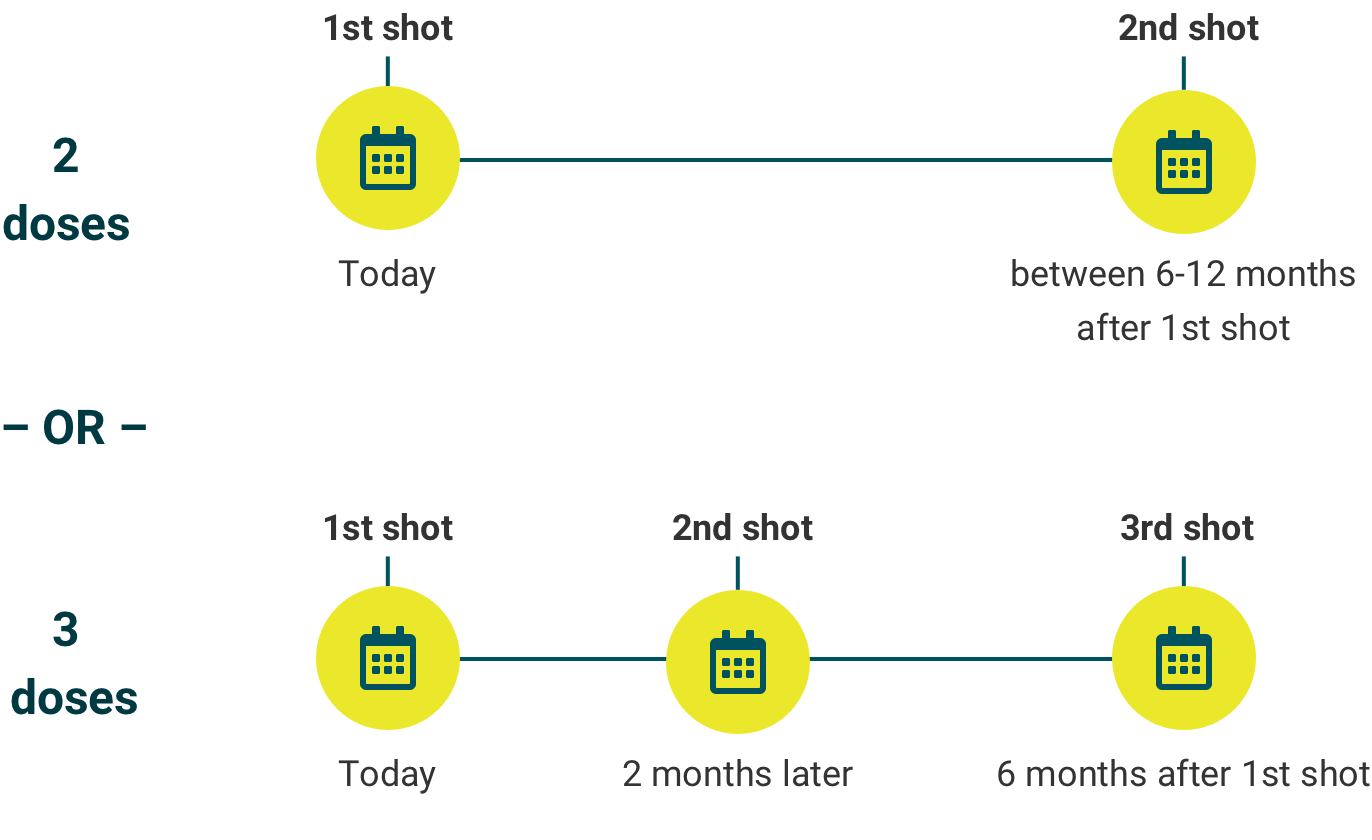
Two-dose schedule
The minimum interval between the first and second doses is 5 months. The second dose may be administered 6 to 12 months after the first dose. If the second dose is given less than 5 months after the first, a third dose is required.
Three-dose schedule
The minimum interval between the first and second doses is 4 weeks; between the second and third doses, 12 weeks; and between the first and third doses, 5 months.
9- to 14-years-old
15- to 45-years-old

Management of Delayed HPV Vaccine Doses
In the event of a delay, there is no need to restart the vaccination series or administer an additional booster dose. The vaccination schedule should simply be resumed from the point at which it was interrupted.
If the first dose was administered before the age of 15 but subsequent doses were delayed until after the 15th birthday, the individual should still complete the two-dose schedule and only one additional dose of the HPV vaccine is required.
Administration of HPV Vaccine
Recommended Route of Administration
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), HPV vaccines must be administered Intramuscularly (only in deltoid and vastus lateralis muscle).
Preferred site
Deltoid muscle of the upper arm
Alternative site
Anterolateral aspect of the thigh
Not acceptable
Intravenous, subcutaneous, or intradermal injection
Site Selection and Safety Considerations
- Intramuscular injection into the deltoid or vastus lateralis minimizes the risk of neurovascular injury.
- Site choice is determined by age, weight, sex, and muscle mass.
- Use of the deltoid is recommended for individuals ≥3 years; the thigh is considered when deltoid administration is not feasible.
Contraindications for Deltoid Administration
- Insufficient muscle volume in the upper arm
- Active skin infection or dermatologic involvement at the injection site
- Requirement for multiple same-day injections in the deltoid region
- Patient preference
Key Recommendations
- Always use a dedicated syringe and needle; avoid mixing with other drugs.
- In patients at risk of bleeding (e.g., hemophilia, anticoagulant therapy), administer the vaccine immediately after anti-hemophilia treatment.
Invalid Administration
- If given subcutaneously or into the gluteal region, the dose is invalid and the vaccination must be repeated intramuscularly in either the deltoid or the anterolateral thigh.
- Subcutaneous injection may result in reduced immune response and increased risk of local adverse effects (induration, erythema, swelling).
Concomitant Administration of HPV Vaccine with Other Vaccines
The HPV vaccine may be administered at the same time as other vaccines. To help manage local adverse effects, such as injection-site pain, it is recommended that the HPV vaccine be given as the last injection when multiple vaccines are administered in a single visit.

